
Sanofi Pasteur (Lyon, France) has produced data showing that its new investigational H5N1 pandemic influenza vaccine containing a proprietary adjuvant achieved a high immune response at the lowest dose of H5N1 antigen reported to date.

Sanofi Pasteur (Lyon, France) has produced data showing that its new investigational H5N1 pandemic influenza vaccine containing a proprietary adjuvant achieved a high immune response at the lowest dose of H5N1 antigen reported to date.

The US Patent & Trademark Office has issued the fifth US patent to MorphoSys AG (Munich, Germany) stemming from MorphoSys’s base HuCAL (human combinatorial antibody library) patent family, providing extended protection to MorphoSys’s core technology.

Five European organizations, including three companies and two hospitals, have joined forces to develop a novel pandemic influenza vaccine as a potential emergency vaccination.

Regulatory agencies have evolved along with the biotechnology industry to define quality standards.

Low-pressure process chromatography could not have developed without immense efforts to resolve scale-up issues in both column design and matrix stability.

In one series of experiments, the glycosylation site of IgG1 was removed and an IgA glycosylation site was introduced-resulting in a total loss of biological function.

It is hoped that HIV patients' own immune responses can be strengthened by vaccines so they will not have to rely exclusively on antiretroviral drugs.

Multivariate data analysis can help biotech manufacturers deepen their process understanding.

In analyzing the industry's current challenges, let's be careful before extrapolating about what they mean.


From the earliest days of the biotechnology industry, companies have grappled with the complexities of making innovative biopharmaceuticals on a large scale. Success in manufacturing begins with process science, since biotech production requires perfection in maintaining living organisms in a sterile environment under controlled physiological conditions. But unless companies can solve the challenge of planning for and managing manufacturing capacity, they will not be able to achieve the full potential of promising biotech products.
For pandemic vaccine processing, single-use filter cartridges and membrane chromatography technologies could offer significant time- and cost-reduction advantages.
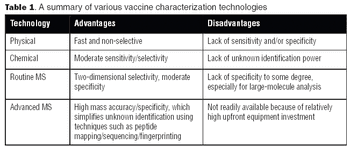
With the advent of high-resolution mass spectrometers and highly sensitive MS instruments, vaccine characterization has entered a new phase.
In animal studies, we have demonstrated that the dose of an injected H5N1 vaccine candidate can be significantly reduced by using a skin patch containing E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) applied over the injection site. LT-activated epidermal Langerhans cells migrate to the nearby draining lymph node and enhance the immune response to the injected antigen. A dry patch formulation has been optimized as a dose sparing strategy for pandemic flu and other vaccines. Iomai Corporation has developed a proprietary stabilizing formulation for the patch that allows use and storage at ambient temperature. The patch withstands temperature extremes during shipment, and is suitable for stockpiling.
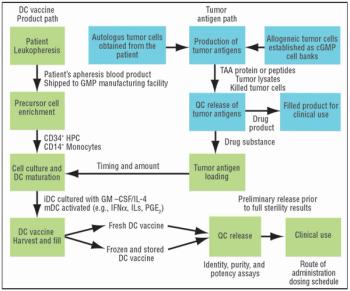
For many cell-based vaccines, the precursor monocytes or CD34+ cells are cultured with cytokines to obtain dendritic cells, which are very potent antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
The recent growth in the vaccine market has led to renewed interest in using adherent human cell lines for vaccine production. Traditionally, small-scale adherent cell line production has been carried out in roller bottles or T-flasks. Over the past few years, however, a number of companies have found multi-tray disposable bioreactors an effective method for producing high-quality drug products using adherent cells. These disposable, expandable systems have also facilitated scale up from laboratory to clinical-scale.

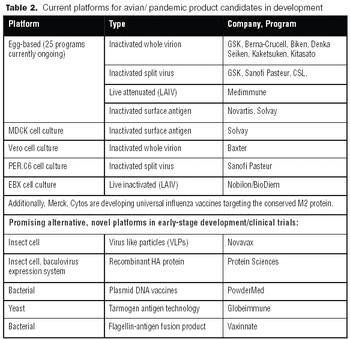
Vaccines against strains originating from avian flu may achieve poor yields in egg-based systems. Consequently, both public and private interest in alternative systems is high.

Any endpoint considered appropriate to support approval, whether a surrogate or a clinical endpoint, must be supported by substantial evidence of effectiveness.
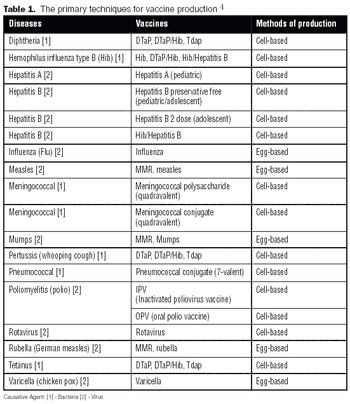
Like the egg-based vaccine production process, producing a vaccine under cGMP conditions using mammalian cells can be a lengthy process, taking a minimum of six to 12 months.
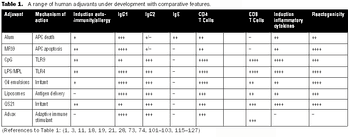
Adjuvant-caused vaccine reactions are one of the most important barriers to better acceptance of routine prophylactic vaccination.

Understanding the end-to-end management of chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) resources provides the opportunity to enhance long-term planning, leverage development options, manage resource trade offs, and track progress against plans. The goal is to improve the pharmaceutical development process to deliver the pipeline. This article provides an overview of the organizational structure of Process Research and Development (PR&D) and the CMC teams at Genentech; the alignment of resources based on CMC contracts, process development activity maps and project resource plans; and the business economic analysis for evaluating development options.
Drug delivery technologies have the potential to enable drug candidates with poor pharmaceutical or biopharmaceutical properties, both for macromolecule and traditional compounds. While there have been many success stories to date, the future offers even more promise. In this article, the author surveys the top ten areas in drug delivery looking forward.

Process development and manufacturing for biopharmaceuticals are often disjointed activities. Disconnects among groups are aggravated by a lack of common terminology and poor data management practices. A UK biotech consortium has initiated a collaborative development effort to address data management issues. The proposed outcome is a data model, based on the ISA-88 Standard for Batch Control, to capture process and facility data throughout the product lifecycle. A data framework that follows the ISA-88 model can simplify process scale up and enable early views of project costs and facility fit.
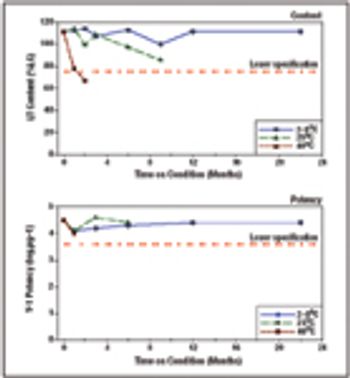
One goal of process characterization is establishing representative performance parameter ranges that can be used to set validation acceptance criteria (VAC). Characterization studies yield varying numbers of data points from multiple experiments, and may also include data generated at different scales (e.g., bench, pilot, and commercial), which add complexity to the analysis. Many statistical approaches can be used to set ranges from large data sets. As an example, we present the statistical considerations and techniques for setting validation acceptance ranges for a chromatography step used in purifying a recombinant protein. Performance parameter data from a combined data set consisting of 67 bench, six pilot, and three full-scale runs were analyzed using the statistical analysis software JMP (SAS Institute). The combined data set was used to compute tolerance intervals, so that sources such as scale and column feed material could be properly modeled. The resulting ranges were used to establish..

This flexible setup minimizes the number of purification process steps, buffers, and process components.