
A symposium at the AAPS National Biotechnology Conference in Boston, June 19-22, 2006, addressed key concerns and new developments in manufacturing biologic products in a sterile environment.


A symposium at the AAPS National Biotechnology Conference in Boston, June 19-22, 2006, addressed key concerns and new developments in manufacturing biologic products in a sterile environment.

"Clinical data is the gold standard" for setting manufacturing specifications, said Patrick Swann, PhD, acting deputy director of the Division of Monoclonal Antibodies at FDA, at a session on specification setting at the AAPS National Biotechnology Conference that was held June 19-21 in Boston.

On August 12, 2003, Johnson & Johnson began recalling certain batches of its anemia drug, Eprex (epoetin alfa, sold as Procrit in the US), in most countries outside of the United States.

The polishing process-unlike capturing-is beginning to benefit from technological advances.

The purpose of the PAT initiative is to move analytical laboratory functions close to the manufacturing process to improve manufacturing efficiency and product quality.
Biotech companies are running into production bottlenecks because standard purification and separation technologies lack the capability to remove the elevated levels of biomass from high titer solutions. Recent developments in filter technology offer the biotech industry a cost-effective solution to processing challenges by reducing bottlenecks, thereby accelerating the time-to-market of new drugs.

Using packed columns in process development activities limits the scope for appraising a large and diverse range of media.

Downstream process design can increase facility output through improved overall process yield or higher batch capacity in mass and volume.

The overall average flux rate for the concentration and diafiltration step was 41 L m–2 h–1.

Air filtration also needs a filter integrity test method to guarantee the sterility of critical parameters.

Transgenics can substantially reduce capital investment and lower production costs through economies of scale and more flexible scale-up.

Disposables can be used for media preparation, clarification, filling in downstream processes . . .

The sugars used to stabilize lyophilized proteins often have not been subjected to appropriate cGMP standards.

The type of reactive moiety controls the site and stability of the covalent link and also the total number of PEGylation sites on a given protein.

In the pharmaceutical industry, ultrafiltration (UF) membranes are used extensively in the downstream purification of recombinant proteins or monoclonal antibodies. However, the fouling of membranes after a unit operation?especially when recombinant proteins or monoclonal antibodies are highly concentrated?is a common problem. Typically, normalized water permeability (NWP) of a membrane can be reduced to about 20 percent of its original permeability at the end of an ultrafiltration-diafiltration (UF-DF) operation.

Extra column effects must be accounted for to make a valid comparison
br> Sterilizing grade, 0.2-µm rated membrane filters are used in many biopharmaceutical processes to ensure the absence of particles and microorganisms from the filtered fluid (1, 2, 3). These filters must meet particular performance criteria in specifically defined applications. For this reason, during filter design, one performance criterion often is enhanced at the expense of another. Consequently, critical process and flow parameters must be defined appropriately to identify the optimal flow membrane filter for a specific application. This paper describes such an evaluation schematic and tests, as well as some common misconceptions.

Cleaning validation is a critical consideration in the pharmaceutical industry. Inadequate cleaning can result in contamination of drug products with bacteria, endotoxins, active pharmaceuticals from previous batch runs, and cleaning solution residues. Such contaminants must be reduced to safe levels, both for regulatory approval and to ensure patient safety.

Operating costs are the white-hot issue in the boardrooms of our life sciences clients and they tend to rule the site selection process. A soft economy, worldwide trade competition, drug cost containment pressures from the US government, and a lean and mean message sent by the venture capital community mean that quantitative factors that focus on the cost of doing business are trumping qualitative lifestyle factors, especially when evaluating sites for a new biopharmaceutical facility.

Is it realistic to believe that tangential flow filtration (TFF), commonly used for concentration, desalting, buffer exchange, and protein fractionation, is now a viable alternative to centrifugation for cell harvest and cell lysate clarification? A new generation of membranes expands the possibilities for TFF as an economical, efficient, high-yielding process substitute, according to this case study?s author.

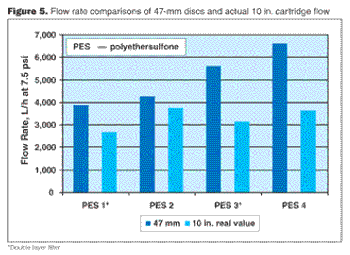
Filterability trials are essential to the successful evaluation of total throughput of single filters or filter combinations. As such, they must be comparable. This case study examines the differences among various devices used and suggests necessary action required to achieve comparability of filterability test trials with 47 mm disc composites.

Pharma industry equipment utilization hovers below 40 percent, which would be an unacceptable figure in most industries.
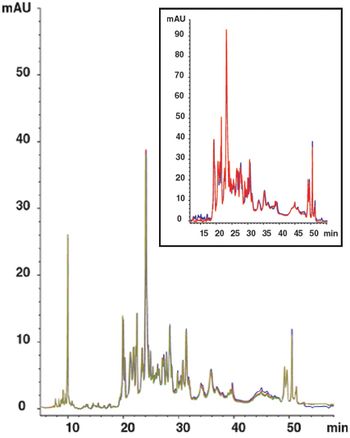
The concentration range of proteins in human plasma spans approximately twelve orders of magnitude, with 85 to 90% of the protein mass distributed across as few as six proteins.

Subcutaneous administration is likely to be an important factor in generating an immunogenic response.
Misinterpreting the effluent profiles obtained during tracer measurements performed for determining packing quality can often lead to excessively large percolation velocities and exaggeration of packing problems. Highly useful and reliable information can be obtained through characterization of tracer effluent curves using the method of moments, information that could be critical for successful scale-up of chromatographic steps. This is the sixth in the "Elements of Biopharmaceutical Production" series.