Validation of analytical methods can be more easily accomplished by breaking the task down into a series of planned steps.

Validation of analytical methods can be more easily accomplished by breaking the task down into a series of planned steps.
The development and optimization process can improve a method, but validation does not. Validation is the final proof that regulations and expectations are met.
Several steps can be taken to maintain test method suitability after the formal completion of the analytical method validation studies,

Two case studies illustrate a systematic approach.

The much needed modernization of the agency's IT systems and inspection capabilities will likely fall prey to budget shortfalls.

Both innovator and generics companies are using analytics to support comparability arguments.

Best practices from Big Biotech, including how to handle new product introductions.
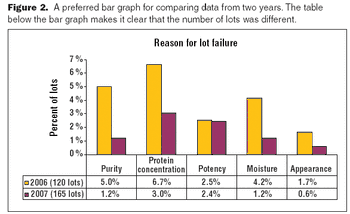
The key to a good graphical presentation is to select the method that best fits the data.
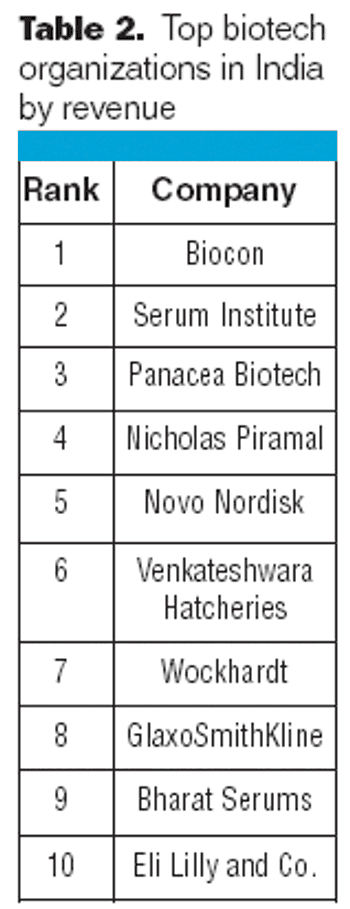
Indian biogenerics could form a major piece of the global biotherapeutics market in the future.

The new year begins on a note of optimism. A major breakthrough in stem cell research promises to open the door to new biomedical research opportunities. The drawn-out Congressional debate over user-fee reauthorization and drug safety regulation is over, and most parties seem satisfied with resulting compromises. The vaccine industry is experiencing a resurgence after years in the doldrums, with important new vaccines on the market and more under development. And unlike many previous years, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had a confirmed commissioner for all of 2007 and relatively stable leadership.

In the process of developing breakthrough biopharmaceuticals with profound therapeutic promise, the many detailed requirements for a successful investigational new drug (IND) submission may seem petty, but they are not. With an IND, you are essentially moving from the cloistered world of the laboratory into a highly regulated industry where details not only matter, but are also greatly magnified by the overriding requirements of safety and efficacy. Treat those details with forethought and you will eventually succeed. Treat them as an afterthought and all of your pioneering science, state-of-the-art technology, and therapeutic ambition could come to nothing. At the very least, your progress to market could be delayed significantly. And if, like most young biopharmaceutical companies, you are on a short financial leash, such delays can be fatal for securing additional funding.

Design space concepts are key to a successful technology transfer.

How the authors used design of experiments and quality by design principles to develop a hydrophobic interaction chromatography step.
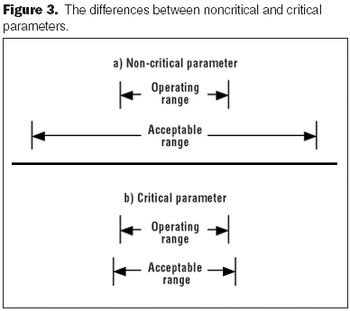
Developing a process validation strategy early in clinical development is critical for a successful validation program.

Many companies acknowledged that Western regulatory standards are tougher than those in China.

The personalized medicine bandwagon is on a roll, offering a new model for calculating reimbursement of high-cost biotech therapies. Strategies for identifying patients who will respond to a certain therapy, as well as those most likely to suffer adverse events, promise to improve healthcare quality while eliminating waste and inappropriate spending. Interventions based on individual genetic characteristics may have limited sales, but support higher prices and less costly clinical research methods.

Congress postpones debate on follow-on biologics while adopting new policies likely to reshape drug development

Contrary to popular belief, the out-of-specification problem started years before the Barr Decision.
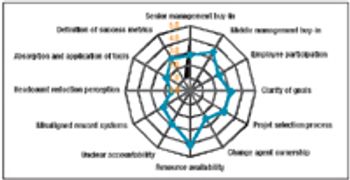
A true visionary leadership is required to drive the progress of operational excellence programs in biopharmaceutical organizations

The industry needs a clear regulatory pathway for the approval of biosimilars.

The upcoming Quality by Design (QbD) pilot program for biotech filings will focus on comparability protocols, Helen Winkle, director of the Office of Pharmaceutical Science at the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, said on September 20, 2007.

Isis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Carlsbad, CA), has purchased Symphony GenIsis for $120 million.

Bayer Schering Pharma AG, (Berlin, Germany) has completed the acquisition of a biologics manufacturing facility in Emeryville, CA, from Novartis.

Discovery Laboratories (Warrington, PA) could see the end of its struggle to launch its Surfaxin (lucinactant) drug on the US market soon, as the manufacturing issues it has faced have been resolved.

PAREXEL Consulting (Boston, MA) has hired three senior GMP consultants based in Europe with the hope of helping its clients address complexities of European Union directives in areas such as manufacturing regulations, quality, and safety.