
Recently, 22 vice presidents of biopharmaceutical operations met in Boston to develop the first operational roadmap for their industry. This special executive-level consortium was organized to discuss two key questions.

Recently, 22 vice presidents of biopharmaceutical operations met in Boston to develop the first operational roadmap for their industry. This special executive-level consortium was organized to discuss two key questions.

A key to bolstering FDA and its mission is securing balanced and consistent funding.

Conducting an analysis of the 4 Ms-man, machine, methods, and materials-enables companies to identify the true root causes of deviations.
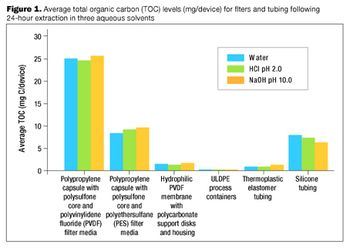
The many benefits of disposable technologies, such as significant savings in time, labor and capital, as well as ease of scalability and flexibility, have led to the growing trend of adopting disposable technologies in bioprocess manufacturing processes.
Biopharmaceutical processes typically require a significant investment in equipment-often a substantial obstacle for start-up companies. The risk of drug development failure is often high, further limiting access to the required capital. Flexibility and lower capital outlays are required not only by start-up companies, but also by research organizations with multiple product lines and by companies requiring quick capacity increases. Disposable technologies offer the highest potential for these companies to meet their business requirements. With lower capital requirements and increased flexibility, disposables are an important part of these companies' risk management strategy.

The deliberate reuse of disposables has caused many clinically significant problems.
In its early days, the biotech industry was almost entirely science driven, but it has since expanded from a laboratory environment to a sophisticated and dynamic manufacturing environment. As technological discoveries are increasingly translated into commercial products, biotech companies are realizing that they must generate a stronger return on assets.

Filtration systems exemplify disposable technologies that can be presterilized.

The number of biotechnology-based human therapeutic products in the late-stage pipeline, and the average cost to commercialize a biotech product, have steadily increased. This has required biotech companies to use economic analysis as a tool during process development and for making decisions about process design. Process development efforts now aim to create processes that are economical, as well as optimal and robust.

FDA is working more closely with foreign regulators to keep abreast of drug and vaccine quality issues in their regions.

If a company wants to reduce costs, it should consider outsourcing some manufacturing and analytical testing to low-cost sites.

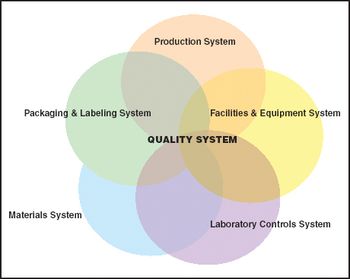
Whether it's for manufacturing drugs, characterizing cell substrates, or regulating new technology, quality systems provide a needed framework.

This article shows how Probabilistic Tolerance Intervals of the form, "We are 99% confident that 99% of the measurements will fall within the calculated tolerance limits" can be used to set acceptance limits using production data that are approximately Normally distributed. If the production measurements are concentrations of residual compounds that are present in very low concentrations, it may be appropriate to set acceptance limits by fitting a Poisson or an Exponential Distribution.

We often assume we know what success looks like for our partner, but we never ask them, or take the time to write it down.

The first part of this article, published in the September 2006 issue, discussed general strategies for validation extensions to other test method components, laboratories and even different test methods.1This second part provides practical tips on how to maintain test method suitability long after the formal completion of analytical method validation (AMV) studies.
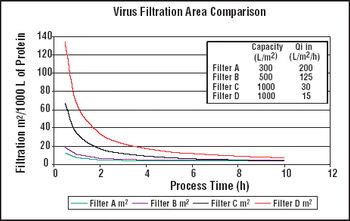
It is important to ensure that flow decay during processing is comparable to that observed during retention studies.

While not yet finalized and adopted, ICH Q10 represents some of the most current thinking with respect to pharmaceuticals manufacturing and control.

Established, fully validated methodology and SOPs are required prior to initiation of any training activities.

Development reports document process development and support the design of validation experiments, yet in many firms training is not provided nor are expectations established. This article describes how project managers can help scientists master the art of report-writing.

SOPs are written job aids that detail the procedure of how to do a specific job task correctly.

The concept of design space has started a minor revolution in our industry.

Reserve samples of test and control articles must be retained for at least one stability time point after the completion of the study.

The challenge is to determine the optimal frequency for preventive maintenance and the optimal frequency and tolerances for calibration readings.

Taking a purist stance is always tempting. It can, however, have unintended consequences.
Companies faced with real or threatened FDA sanctions are usually least prepared to react effectively.