
FDA's approach involves adopting efficient strategies for targeting inspections to more high-risk operations likely to have the greatest impact on public health.

FDA's approach involves adopting efficient strategies for targeting inspections to more high-risk operations likely to have the greatest impact on public health.

Following the US Senate approval of the FDA Revitalization Act (FDARA, S.1082) in May, the debate over drug safety and the reauthorization of the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA) now moves to the House.

Membrane-based chromatography technologies sometimes offer advantages over resin-based technologies.

The information provided by analytical testing is important in determining whether additional clinical trails are necessary to bring a follow-on to market.

Lax enforcement arising from a lack of political will creates the potential for a loss of public confidence.

In March, the US Food and Drug Administration released a new draft guidance, along with its guidance agenda for the year.

Neotropix, Inc. (Malvern, PA, www.neotropix.com), a biotechnology company dedicated to the development and commercialization of virus-based therapeutics for the treatment of cancer and other diseases, received a warning letter (http://www.fda.gov/foi/warning_letters/b6308d.pdf) on March 23, 2007, citing deviations from good laboratory practices (GLP) regulations governing the proper conduct of nonclinical studies as published under 21 CFR Part 58.
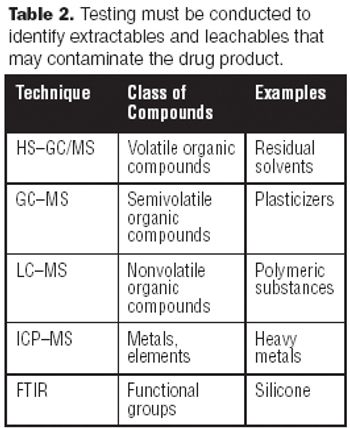
A tremendous amount of analytical testing is required to support a biopharmaceutical product from discovery, development, and clinical trials, through manufacturing and marketing. Numerous methods are used to fully characterize large molecules because of their complexity-characterizing them is significantly more difficult than it is for small molecules. Biopharmaceuticals are produced via living systems, i.e., E. coli, yeast, or mammalian cells, which require additional testing matrices.

The challenge will be to design a system that is flexible, yet appropriate, for the broad range of biological products and the varying quality control capabilities of different manufacturers.

Process monitoring ensures that the process performs within the defined acceptable variability that served as the basis for the filed design space.

Scale-up issues leading to long development times and deviations in the commercial facility is a critical challenge.

The biopharmaceutical industry has gained a lot of experience in monitoring glycosylation, but still has a lot to learn about the structure–function relationship.

The US Food and Drug Administration (Rockville, MA, www.fda.gov) commemorated its 100th anniversary in 2006 as America's premier public health agency aimed at protecting and promoting public health.

The United States Pharmacopeia (USP, Rockville, MD, www.usp.org) and the UK's National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC, Hertfordshire, UK, www.nibsc.ac.uk) are seeking participants in a study of analytical methods used by the industry to characterize and quantify oligosaccharides.

All contributors to the process should have a clear understanding of their capacity and see their work activities as a priority, regardless of where they fall on the critical path.

Disposables are no longer a mistrusted new technology; they're seen as a potential solution to everyday problems.

Although IP due diligence is relevant to virtually any transaction between biotech companies, a detailed investigation into IP assets is particularly critical to M&A transactions.

An underlying theme of FDA's drug safety program is that new discoveries in biomedical science can detect risk issues earlier in clinical development.
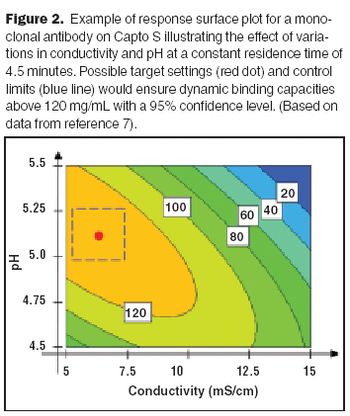

A series of ICH guidances are encouraging industry to adopt quality-based approaches for achieving the "desired state" of drug and biotech manufacturing: more efficient and flexible operations that can reliably produce high quality therapies with less regulatory oversight.

The recent FDA decision that meat from cloned animals is safe for human consumption seems logical enough. A protein is a protein. But even if we can eat such meat, it doesn't necessarily make economic or ecological sense to do so.

Utility patents are granted to anyone who invents any new and useful process, machine, article of manufacture, composition of matter, or any new improvement thereof.

The pharmaceutical industry is well aware that FDA is trying to take a risk-based approach to enforcing the current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) regulations. This approach is driven by an economic reality: FDA simply does not have the resources to inspect every facility every other year. The organization doesn't even have the resources to inspect facilities every three years. Likewise, it is not cost-effective for our companies to carry out a complete, documentation-oriented revalidation for every process change, regardless of its significance or risk.

All of the primary unit operations for cell culture and purification had scores greater than the action threshold.

The HSV-1 and HVP-2 titers were determined by the inoculation of test solutions into Vero cell cultures and calculated using the Reed M?ench method.