
Wyeth today relies on biotech product revenue to drive approximately 25% of its revenues.

Wyeth today relies on biotech product revenue to drive approximately 25% of its revenues.

Understand your company's requirements, define responsibilities,and manage your team effectively.

Is it possible to reconcile phage therapy, which is inherently variable, with requirements for tight product characterization and control?

FDA did not gain any real teeth for regulating unsafe and ineffective products until a national health disaster in 1937 roused a public outcry.

Congress is not considering legislation that would expand FDA authority to regulate biologics.
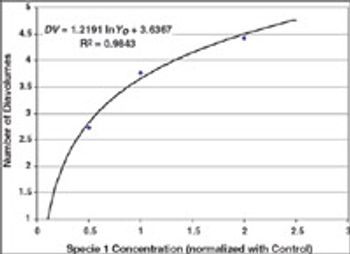
Case studies were run to test Process Analytical Technology applications for protein refolding, diafiltration, and cation exchange chromatography. It is shown that it is feasible to design control schemes that rely on measurement of product quality attributes and thereby enable real-time decisions.
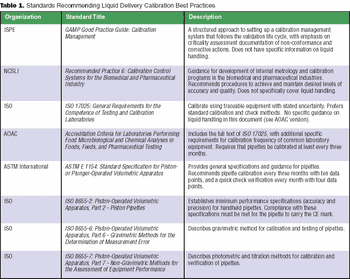
Federal regulations are broad and open to interpretation. Most have not caught up with advancements in technology.
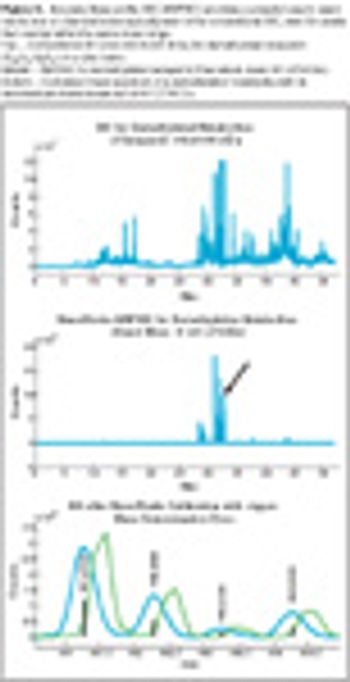
A novel calibration approach was developed that not only calibrates the X-axis, but also calibrates the peak shape.

For decades now, it has been said that "the process is the product" for biologics. Great care and consistency must be applied in their upstream manufacture-during fermentation, harvest, and early purification-to preserve their complex structure, which confers their activity and specificity. As the product moves to late-stage purification, however, the relative concentration of impurities and altered product forms is diminished. Also, the final dosage form of most large molecule biopharmaceuticals is the relatively simple liquid formulation of parenteral dosage form. In contrast, manufacturing the solid dosage forms common for small-molecule drugs involves more complex processes, such as mixing dry powders, granulation, manufacturing controlled-release matrices, and tableting.

Food and Drug Administration is encouraging public–private collaborations to more fully explore the physical and chemical characteristics of nanoparticles.

A symposium at the AAPS National Biotechnology Conference in Boston, June 19-22, 2006, addressed key concerns and new developments in manufacturing biologic products in a sterile environment.

"Clinical data is the gold standard" for setting manufacturing specifications, said Patrick Swann, PhD, acting deputy director of the Division of Monoclonal Antibodies at FDA, at a session on specification setting at the AAPS National Biotechnology Conference that was held June 19-21 in Boston.

Protein aggregation is a term that can include many types of aggregation, from rapidly reversible aggregation caused by non-covalent bonds to irreversible aggregation in the form of covalent oligomers.

On August 12, 2003, Johnson & Johnson began recalling certain batches of its anemia drug, Eprex (epoetin alfa, sold as Procrit in the US), in most countries outside of the United States.

The purpose of the PAT initiative is to move analytical laboratory functions close to the manufacturing process to improve manufacturing efficiency and product quality.

Without generic competition, the US is at risk of losing its position of leadership in biopharmaceuticals.

The belief that glycosylation is critical to ensuring the functionality of protein therapeutics-and preventing immunogenicity-drives many manufacturing decisions. But is it time to question this industry tenet?

The overhead expense that comes along with each new enterprise application adds up quickly, and can be somewhat invisible to owners of the system.

Air filtration also needs a filter integrity test method to guarantee the sterility of critical parameters.

Glavin is preparing a plan to modernize ORA through organizational changes . . .

Motorola recognized that vartion is the death knell of any process, so the company established a methodology called Six Sigma

The sugars used to stabilize lyophilized proteins often have not been subjected to appropriate cGMP standards.

After reading Brian O'Connell's column in the February 2006 issue of BioPharm International, entitled, "Will Venture Capital Firms Turn Their Backs on Stem-Cell Research?" one would like to comment. The press is too fascinated by Dr. Hwang's scientific misconduct, which was discovered, and sanctions imposed.
The Food and Drug Administration recently unveiled its long-awaited Critical Path Opportunities List, which maps out a number of "scientific projects" for improving the testing and production of biotech therapies. In its March report, FDA recognizes that problems in the characterization, testing, and quality management of medical products can delay clinical trials and even completely block drug development.

RFID is currently the most advanced tracking technology, but manufacturers need to pursue a multilayered approach . . .