Using multivariate experiments to define acceptable ranges.

Using multivariate experiments to define acceptable ranges.
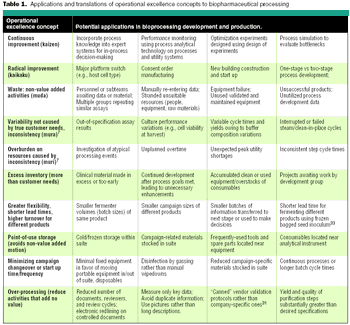
Translate the concepts in to practical applications and reduce waste.
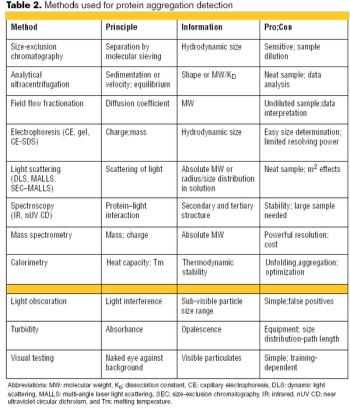
FDA perspectives on specs and effective control strategies.

The FDA and other regulatory authorities are evaluating new regulations to ensure the safety and quality of nanomaterials in biomedical products.
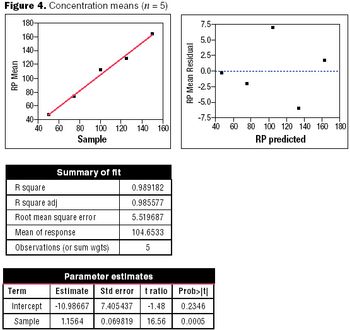
Well-designed experiments can reduce the risk of coming to an incorrect conclusion during a process characterization, assay validation, or process validation study.

Supplemental tables for the above-mentioned article, providing additional information about the application of operational excellence methods.

A centralized quality control strategy may be the best solution.

The country is reeling from US Treasury Secretary Henry Paulson's proposed $700 billion Wall Street bailout. In appealing for support, Paulson stressed this was a crisis. This sense of urgency is reminiscent of the way millions of Americans without health insurance cope with medical problems-in the emergency room, because they have no access to routine and preventive care.

The FDA's QbD pilot program is supporting good manufacturing on a global basis.

Despite the current regulatory uncertainty, pharmaceutical companies should move forward with planning for serialization and pedigree.

Statistical methods for calculating confidence intervals, tolerance intervals, and capability analysis to reduce out-of-specification situations.

Every biotech company reaches a point in its development where it must decide what path it will take after it passes the start-up phase. This article discusses what the company must consider to decide what business model it will follow.

The heparin debacle and other crises involving imported drugs and biologics has put pressure on the US FDA to step up its oversight of foreign drug manufacturing.

Risk mitigation should be a key aspect of any contract manufacturing organization's business strategy.

The complexity of Quality by Design leads naturally to questions of how much work it requires, how many companies have the resources to do it, and what the payoff is for anybody.

GMPs in Phase 1 is more important now than ever before.
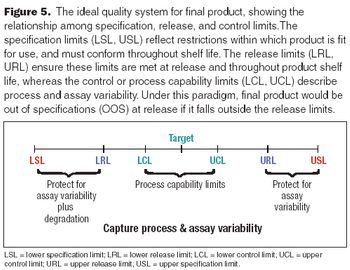
Set limits to provide incentives for process improvements.

Manufacturers of biopharmaceuticals can improve productivity by taking patient wellness into account.
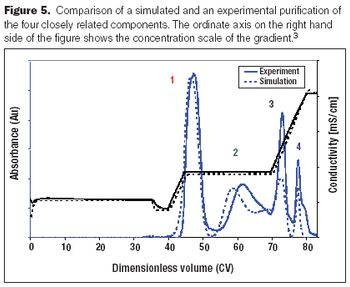
A review of some recent contributions in process chromatography.

The Sentinel System aims to generate more adverse event reporting by health professionals, to analyze health information more effectively, and to enhance FDA methods for communicating new safety information to providers and patients.

Enough Republicans sided with Democrats last month to approve legislation canceling a scheduled 10.6% cut in Medicare fees for physicians. In doing so, the legislators tacked on dozens of provisions pleasing to beneficiaries and providers alike.

The FDA is launching a pilot program to allow manufacturers to electronically file drug establishment registration and drug listing information, such as ingredients, labeling, and manufacturing information.
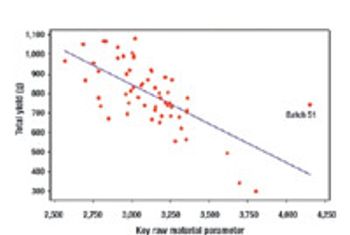
Quality by Design and Design Space can be used by companies to enhance process understanding, improve scientific rigor, and enhanced qualitative and quantative performance, as well as cost savings.

The US Food and Drugs Administration is boosting its efforts for orphan drugs development.

Best practices a pharmaceutical company can follow to execute their strategy sucessfully.