
PAREXEL Consulting (Boston, MA) has hired three senior GMP consultants based in Europe with the hope of helping its clients address complexities of European Union directives in areas such as manufacturing regulations, quality, and safety.

PAREXEL Consulting (Boston, MA) has hired three senior GMP consultants based in Europe with the hope of helping its clients address complexities of European Union directives in areas such as manufacturing regulations, quality, and safety.

SAFC (St. Louis, MO), a member of the Sigma-Aldrich Group, has announced a $29-million investment to significantly expand its drug substance capabilities in high-potency biologics at the Sigma-Aldrich facility in Jerusalem, Israel

The US Patent & Trademark Office has issued the fifth US patent to MorphoSys AG (Munich, Germany) stemming from MorphoSys’s base HuCAL (human combinatorial antibody library) patent family, providing extended protection to MorphoSys’s core technology.

Bristol-Myers Squibb (Princeton, NJ) will acquire privately held Adnexus Therapeutics (Waltham, MA), the developer of a new therapeutic class of biologics called Adnectins.

Five European organizations, including three companies and two hospitals, have joined forces to develop a novel pandemic influenza vaccine as a potential emergency vaccination.

Regulatory agencies have evolved along with the biotechnology industry to define quality standards.

Favrille, a San Diego-based biopharmaceutical company, is one of a handful of firms on the forefront of personalized medicine. Because personalized treatment is tailored to an individual's biology, it has the potential to be far more effective than current approaches to disease management.

It became a strategic imperative to find a better, more efficient way to manufacture our products. To continue with the status quo was untenable.

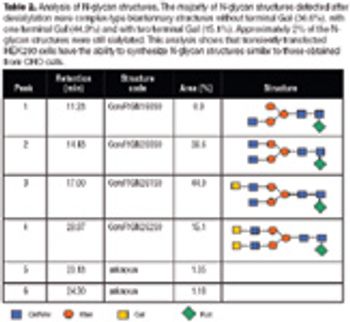
In one series of experiments, the glycosylation site of IgG1 was removed and an IgA glycosylation site was introduced-resulting in a total loss of biological function.

It is hoped that HIV patients' own immune responses can be strengthened by vaccines so they will not have to rely exclusively on antiretroviral drugs.

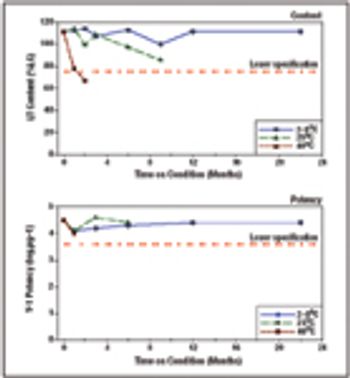
Multivariate data analysis can help biotech manufacturers deepen their process understanding.

The BIOSTAT Cultibag RM is a disposable bioreactor that combines rocking motion mixing technology with Sartorius engineered control capabilities.



From the earliest days of the biotechnology industry, companies have grappled with the complexities of making innovative biopharmaceuticals on a large scale. Success in manufacturing begins with process science, since biotech production requires perfection in maintaining living organisms in a sterile environment under controlled physiological conditions. But unless companies can solve the challenge of planning for and managing manufacturing capacity, they will not be able to achieve the full potential of promising biotech products.

The US Food and Drug Administration's Nanotechnology Task Force (www.fda.gov/nanotechnology/ nano_tf.html) has released a report recommending the agency develop guidelines and take other steps to address the benefits and risks of products, including drugs and medical technology, that use nanotechnology.
For pandemic vaccine processing, single-use filter cartridges and membrane chromatography technologies could offer significant time- and cost-reduction advantages.
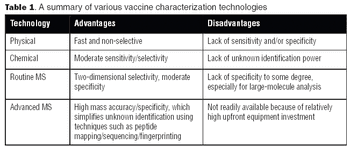
With the advent of high-resolution mass spectrometers and highly sensitive MS instruments, vaccine characterization has entered a new phase.
In animal studies, we have demonstrated that the dose of an injected H5N1 vaccine candidate can be significantly reduced by using a skin patch containing E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) applied over the injection site. LT-activated epidermal Langerhans cells migrate to the nearby draining lymph node and enhance the immune response to the injected antigen. A dry patch formulation has been optimized as a dose sparing strategy for pandemic flu and other vaccines. Iomai Corporation has developed a proprietary stabilizing formulation for the patch that allows use and storage at ambient temperature. The patch withstands temperature extremes during shipment, and is suitable for stockpiling.
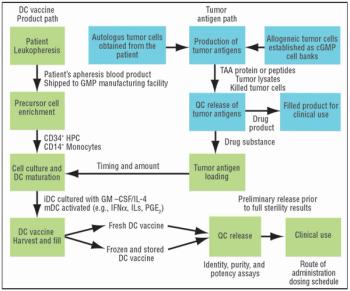
For many cell-based vaccines, the precursor monocytes or CD34+ cells are cultured with cytokines to obtain dendritic cells, which are very potent antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
The recent growth in the vaccine market has led to renewed interest in using adherent human cell lines for vaccine production. Traditionally, small-scale adherent cell line production has been carried out in roller bottles or T-flasks. Over the past few years, however, a number of companies have found multi-tray disposable bioreactors an effective method for producing high-quality drug products using adherent cells. These disposable, expandable systems have also facilitated scale up from laboratory to clinical-scale.

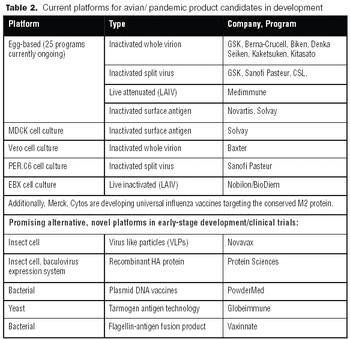
Vaccines against strains originating from avian flu may achieve poor yields in egg-based systems. Consequently, both public and private interest in alternative systems is high.

Any endpoint considered appropriate to support approval, whether a surrogate or a clinical endpoint, must be supported by substantial evidence of effectiveness.
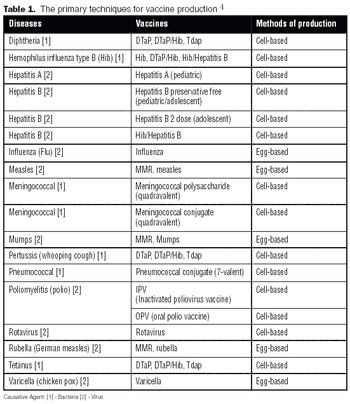
Like the egg-based vaccine production process, producing a vaccine under cGMP conditions using mammalian cells can be a lengthy process, taking a minimum of six to 12 months.
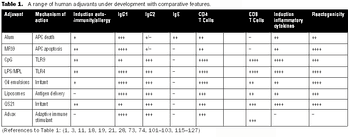
Adjuvant-caused vaccine reactions are one of the most important barriers to better acceptance of routine prophylactic vaccination.