
Disposables are no longer a mistrusted new technology; they're seen as a potential solution to everyday problems.

Disposables are no longer a mistrusted new technology; they're seen as a potential solution to everyday problems.

An underlying theme of FDA's drug safety program is that new discoveries in biomedical science can detect risk issues earlier in clinical development.

A series of ICH guidances are encouraging industry to adopt quality-based approaches for achieving the "desired state" of drug and biotech manufacturing: more efficient and flexible operations that can reliably produce high quality therapies with less regulatory oversight.

The recent FDA decision that meat from cloned animals is safe for human consumption seems logical enough. A protein is a protein. But even if we can eat such meat, it doesn't necessarily make economic or ecological sense to do so.

The pharmaceutical industry is well aware that FDA is trying to take a risk-based approach to enforcing the current good manufacturing practices (cGMP) regulations. This approach is driven by an economic reality: FDA simply does not have the resources to inspect every facility every other year. The organization doesn't even have the resources to inspect facilities every three years. Likewise, it is not cost-effective for our companies to carry out a complete, documentation-oriented revalidation for every process change, regardless of its significance or risk.

All of the primary unit operations for cell culture and purification had scores greater than the action threshold.

The HSV-1 and HVP-2 titers were determined by the inoculation of test solutions into Vero cell cultures and calculated using the Reed M?ench method.

How much do regulatory agencies know about nanotechnology or microfluidics? Yesterday, the answer was probably, "not much." Tomorrow, it may be "a lot." The reason is that new technologies push the agencies to expand their expertise.

FDA is encouraging broader use of pharmacogenomic data by offering manufacturers early informal advice.

The prospect of any cost savings has been fueling efforts to establish a pathway for follow-on biopharmaceuticals.

Vagueness in the ICH Q2A and Q2B guidelines necessitates effective protocol design and data analysis. For specificity (detection in the presence of interfering substances), the goal is statistical differences with meaningful implications on assay performance. Linearity (results directly proportional to concentration of analyte in the sample) is typically demonstrated via least squares regression. Accuracy (difference between measured and true values) usually is presented as a percent of nominal. Precision analysis is vital because it supports claims of accuracy and linearity. A well-designed experiment and statistically relevant methods will facilitate method validation in accordance with ICH guidelines.

In various races in the November elections, voters supported stem cell research. Now, will they prepared to fund it?

Conducting an analysis of the 4 Ms-man, machine, methods, and materials-enables companies to identify the true root causes of deviations.
The many benefits of disposable technologies, such as significant savings in time, labor and capital, as well as ease of scalability and flexibility, have led to the growing trend of adopting disposable technologies in bioprocess manufacturing processes.
Biopharmaceutical processes typically require a significant investment in equipment-often a substantial obstacle for start-up companies. The risk of drug development failure is often high, further limiting access to the required capital. Flexibility and lower capital outlays are required not only by start-up companies, but also by research organizations with multiple product lines and by companies requiring quick capacity increases. Disposable technologies offer the highest potential for these companies to meet their business requirements. With lower capital requirements and increased flexibility, disposables are an important part of these companies' risk management strategy.
The adoption of single-use containers in the biopharmaceutical industry is becoming more frequent as the popularity and availability of the technologies increase. The choice of a solution for storage in single-use containers clearly depends on the application and the inherent risks associated with the application. A "one fits all" single-use system cannot respond to all the requirements of a particular step in a biopharmaceutical process, much less to all the steps of a process. The needs of an application will lead to very specific single-use solutions.

The deliberate reuse of disposables has caused many clinically significant problems.
In its early days, the biotech industry was almost entirely science driven, but it has since expanded from a laboratory environment to a sophisticated and dynamic manufacturing environment. As technological discoveries are increasingly translated into commercial products, biotech companies are realizing that they must generate a stronger return on assets.

Filtration systems exemplify disposable technologies that can be presterilized.

FDA is working more closely with foreign regulators to keep abreast of drug and vaccine quality issues in their regions.

Whether it's for manufacturing drugs, characterizing cell substrates, or regulating new technology, quality systems provide a needed framework.

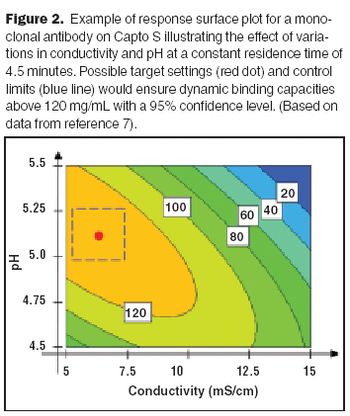
This article shows how Probabilistic Tolerance Intervals of the form, "We are 99% confident that 99% of the measurements will fall within the calculated tolerance limits" can be used to set acceptance limits using production data that are approximately Normally distributed. If the production measurements are concentrations of residual compounds that are present in very low concentrations, it may be appropriate to set acceptance limits by fitting a Poisson or an Exponential Distribution.

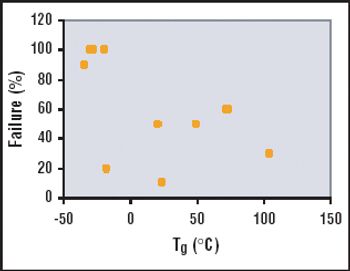
The first part of this article, published in the September 2006 issue, discussed general strategies for validation extensions to other test method components, laboratories and even different test methods.1This second part provides practical tips on how to maintain test method suitability long after the formal completion of analytical method validation (AMV) studies.
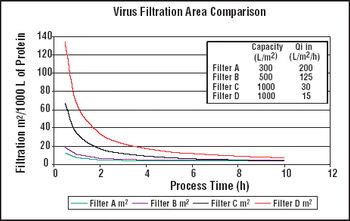
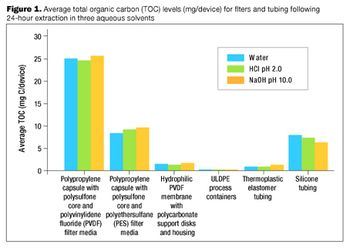
It is important to ensure that flow decay during processing is comparable to that observed during retention studies.