The future of therapeutic MAbs lies in the development of economically feasible downstream processes.

The future of therapeutic MAbs lies in the development of economically feasible downstream processes.

New techniques can overcome bottlenecks in existing facilities.
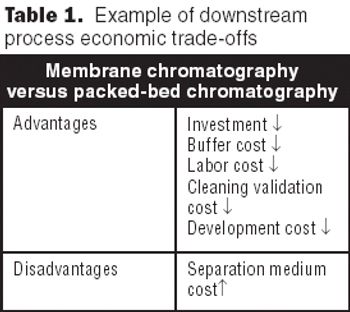
A purification scheme to maximize the efficiency of the purification process and product purity while minimizing the development time for early-phase therapeutic antibodies.
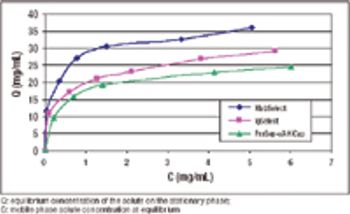
A stable alternative to Protein A chromatography.
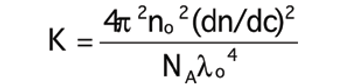
Can increase in ionic strength result in higher viscosity?
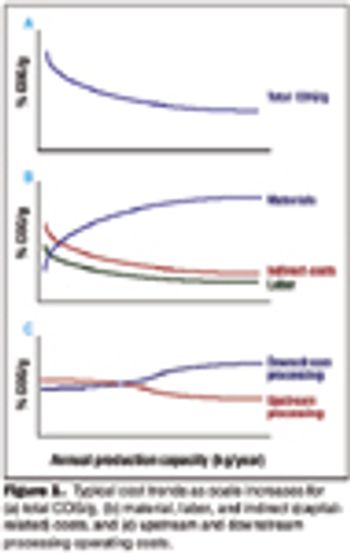
The future of therapeutic MAbs lies in the development of economically feasible downstream processes.

Altering the order of operations, using new resins, and increasing dynamic binding capacity can obviate the need for major facilty changes.

A purification scheme to maximize the efficiency of the purification process and product purity while minimizing the development time for early-phase therapeutic antibodies.
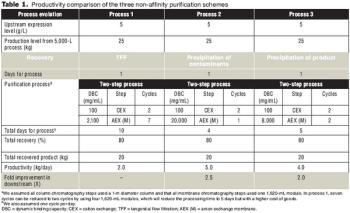
In three non-affinity purification processes based on cation exchange capture with high binding capacity, applying a host cell protein exclusion strategy enabled robust scale up and better economics.
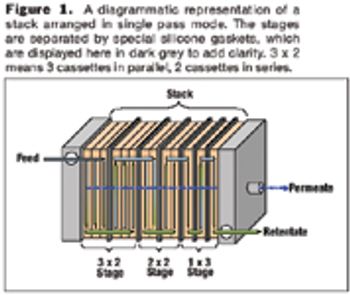
New techniques can greatly improve the MAb purification process.
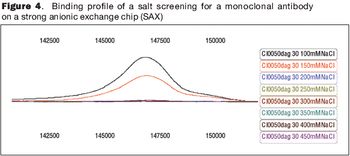
The future of therapeutic MAbs lies in the development of economically feasible downstream processes.

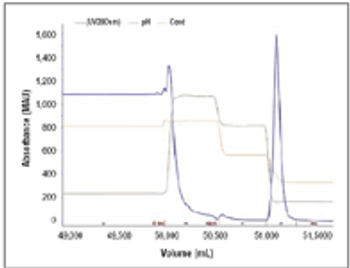
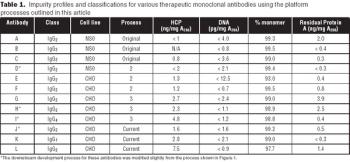
Results from a process developed for a commercial antibody.
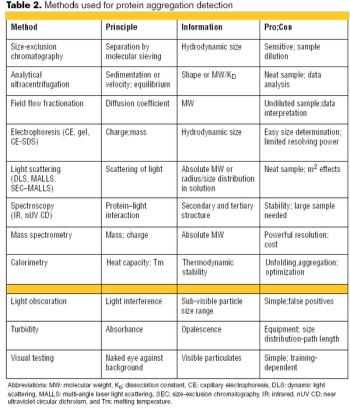
FDA perspectives on specs and effective control strategies.
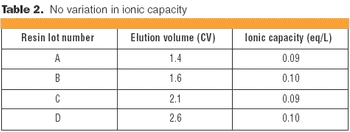
Understanding the impact on process performance.

In the context of process validation, the confirmation of a belief must be checked repeatedly, throughout the product lifecycle.
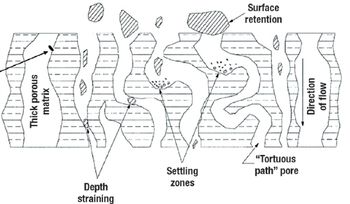
A comparison of primary harvest techniques.

The book is a useful, comprehensive, and truly an excellent reference source of biopharmaceutical information.
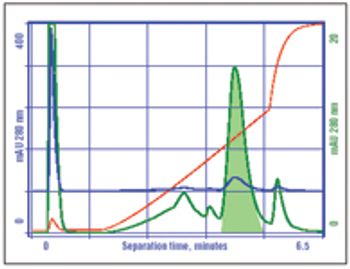
Manufacturing challenges surround the use of IgM monoclonal antibodies, but these can be overcome with current technology.
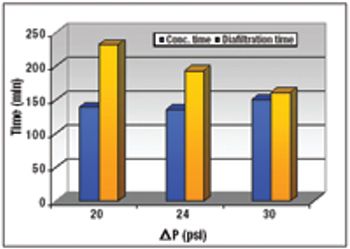
An alternative approach to traditional Protein A schemes is comparable in overall efficiency, product recovery, and quality.
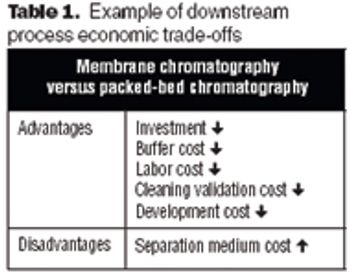
The future of therapeutic MAbs lies in the development of economically feasible downstream processes.
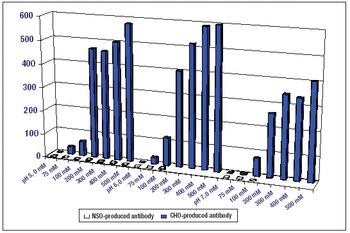
If certain engineering challenges can be addressed, precipitation may prove to be a valuable tool for antibody purification.
When platform processes are applied to fusion molecules, innovation and flexibility are needed.

Crucell N.V. (Leiden, the Netherlands) has discovered a set of human monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) that work to neutralize and protect against H5N1.

The US Patent & Trademark Office has issued the fifth US patent to MorphoSys AG (Munich, Germany) stemming from MorphoSys’s base HuCAL (human combinatorial antibody library) patent family, providing extended protection to MorphoSys’s core technology.