
Today, most disposables are used for process development and clinical-scale manufacturing. Substantial growth in disposables usage may not occur until disposables are incorporated into the production of licensed products at commercial scale.

Today, most disposables are used for process development and clinical-scale manufacturing. Substantial growth in disposables usage may not occur until disposables are incorporated into the production of licensed products at commercial scale.

Discrete simulation allows the design teams to see every meaningful detail about equipment and materials flowing through the process.

Eden Biodesign (Liverpool, UK, www.edenbiodesign.com), SAFC (St. Louis, MO, www.sigmaaldrich.com/SAFC/Pharma), Midatech Group (Oxfordshire, OX, www.midatechgroup.com), Cellexus Systems (Cambridgeshire, UK, www.cellexusbiosystems.com), and BioConvergence LLC (Bloomington, IN, www.bioc.us) are sprucing up their product development and services with the construction of new manufacturing facilities.

Venture capital insiders say that the flow of funds into biopharma shouldcontinue, driven by the large amount of money available for investment.
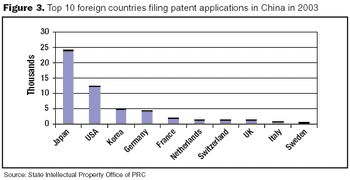
China's central government is aware of the need to improve intellectual property protection and enforcement.

By outsourcing high-end processes that demand advanced analytical and technical skills, biopharm companies are reaping substantial savings.

Lax enforcement arising from a lack of political will creates the potential for a loss of public confidence.

Abbott (Abbott Park, IL, www.abbott.com) recently announced the official opening of its new biologics manufacturing facility in Puerto Rico to support the long-term supply of its leading biologic agent, HUMIRA (adalimumab), and other future biologics.

Singapore's efforts to grow its biologics manufacturing sector received a significant boost on March 28, 2007, when the Singapore Economic Development Board (EDB) announced that Genentech, Inc. (San Francisco, CA, www.gene.com) has decided to establish a commercial-scale microbial-based biologics manufacturing facility in Singapore.

Partnering with a surging number of CROs, CMOs, CSOs, and other niche providers, biopharm companies in 2007 will have an estimated spend of more than $7 billion on international clinical trial outsourcing alone.
The greatest benefits of outsourcing are realized when a company takes a strategic approach rather than a tactical approach.

The contract manufacturer must have sufficient capacity so it can absorb possible surge in demand, and back-up capability in case of a power failure or other event.

Financial pressure to show short-term results also affects the pharmaceutical industry, from Big Pharma to small biotech.
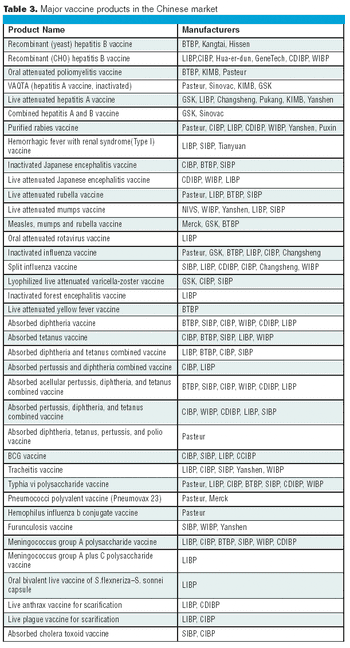
The Chinese vaccine market competition is now transferring from the former price-competition model to a technology- competition model.

This 1,230-page tome is a must-have encyclopedia for any person or organization planning to interact with the biopharmaceutical market in China. It contains 23 well-written chapters and five appendices written by individuals who are experts in the areas they address. Some of these experts are not well known in the US; thus the book also provides an excellent introduction to people whose knowledge and opinions are important when considering biopharmaceuticals in China. Many chapters were translated from Chinese and this is the first time that their information has been provided to the West.

Virtually every corner of the United States (not to mention the rest of the world) seeks to build a powerful biotech presence (see www.bio.org/local/). Since the dawn of biotechnology in the mid 1970s, private venture capital, major corporations, and state and federal governments have poured hundreds of billions of dollars into the industry. Results have been mixed, in terms of benefits to local economies and products that reached the marketplace.

Scale-up issues leading to long development times and deviations in the commercial facility is a critical challenge.

Cities, counties, states; every political entity in our country is driving to develop a biotechnology presence in its respective region.

All contributors to the process should have a clear understanding of their capacity and see their work activities as a priority, regardless of where they fall on the critical path.

Disposables are no longer a mistrusted new technology; they're seen as a potential solution to everyday problems.

Although IP due diligence is relevant to virtually any transaction between biotech companies, a detailed investigation into IP assets is particularly critical to M&A transactions.

The Chinese government's investments in the biopharmaceutical sector may help it become one of the leading industries in China by 2020.
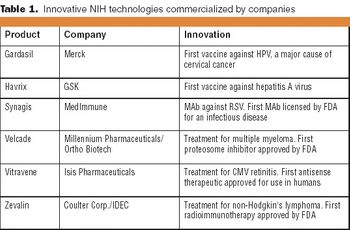
NIH makes available a full range of licenses for commercial evaluation and for the sale of commercial products and services.

Utility patents are granted to anyone who invents any new and useful process, machine, article of manufacture, composition of matter, or any new improvement thereof.

In the September 2006 issue I wrote about the ticklish issue of CEO pay and how shareholder groups, especially the powerful pension and other institutional groups, are growing sick and tired of CEO overpayment and underperformance.