
Stiffer enforcement of quality standards aims to restore public confidence in agency actions.

Stiffer enforcement of quality standards aims to restore public confidence in agency actions.
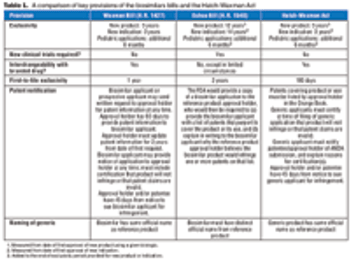
The introduction of two rival bills has intensified the long-simmering debate on biosimilars regulation in the US.

The truth is, we should have been afraid of H1N1, because the threat of a flu pandemic is real.

Agency officials promise swift action against violators of drug safety and quality regulations.

Importing foreign drugs is not the best way to increase access to medicine. The risks are too high, and it burdens the over-stretched FDA unfairly.

Avoiding healthcare reform is not the best option for the pharmaceutical industry.

How change plays out will depend not only on the new Whitehouse, but on pharma leaders' ability to adapt to changing times.

The FDA's QbD pilot program is supporting good manufacturing on a global basis.

The Sentinel System aims to generate more adverse event reporting by health professionals, to analyze health information more effectively, and to enhance FDA methods for communicating new safety information to providers and patients.

The FDA is launching a pilot program to allow manufacturers to electronically file drug establishment registration and drug listing information, such as ingredients, labeling, and manufacturing information.

The FDA is under attack from all sides. Many influential members of Congress either don't trust the agency to monitor the industry appropriately, or have found it politically expedient to keep sounding alarms about inadequate oversight of food and drug safety and clinical research. The good news is that there seems to be a growing consensus that FDA needs a major infusion of cash to regain its stature as an effective science-based regulatory agency.

The heparin safety crisis puts a spotlight on manufacturing processes and regulatory oversight.

More informed submissions may lead to regulatory flexibility for postapproval changes.

The expanding globalization of the industry poses a challenge for international enforcement.

Following the partial recall initiated on January 25, 2008, Baxter Healthcare has expanded its recall of heparin.

Congress postpones debate on follow-on biologics while adopting new policies likely to reshape drug development

The US Patent & Trademark Office has issued the fifth US patent to MorphoSys AG (Munich, Germany) stemming from MorphoSys’s base HuCAL (human combinatorial antibody library) patent family, providing extended protection to MorphoSys’s core technology.

Federal regulation of biologics began more than 100 years ago with the enactment of the Biologics Control Act of 1902. That act required licensing of establishments to manufacture and sell vaccines, sera, antitoxins, and other similar products in order to prevent deaths from contaminated vaccines, as had recently occurred with the diphtheria antitoxin.

The new legislation authorizes the use of fee revenues for drug safety oversight and assessment throughout a product's lifecycle.

The US Food and Drug Administration's Nanotechnology Task Force (www.fda.gov/nanotechnology/ nano_tf.html) has released a report recommending the agency develop guidelines and take other steps to address the benefits and risks of products, including drugs and medical technology, that use nanotechnology.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA, Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) issued a revised draft guidance on July 20 to help ensure that the safety, purity, and potency of biologics products is not compromised as a result of innovative, flexible manufacturing arrangements.

Any endpoint considered appropriate to support approval, whether a surrogate or a clinical endpoint, must be supported by substantial evidence of effectiveness.

In late June and early July, the US Congress moved forward on three important bills affecting the biopharmaceutical industry, related to follow-on biologics, the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA), and the 2008 FDA budget.

The FDA issued MedImmune, Inc. (Gaithersburg, MD, www.medimmune.com), a warning letter for violating the agency's manufacturing rules and held off approving the company's influenza vaccine for use in children younger than age five until the problems are resolved.

The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA, Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) has issued final recommendations for increasing the supply of safe and effective influenza vaccines for both seasonal and pandemic use.