Biopharmaceutical Analysis
Latest News

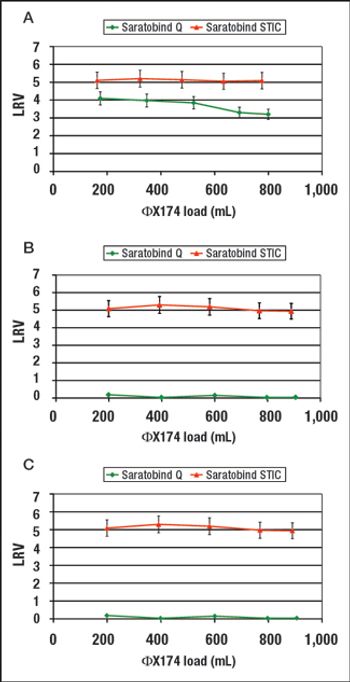
STIC allows polishing to be carried out without an interstitial dilution step, which reduces process time and avoids additional buffer preparation and hold steps.
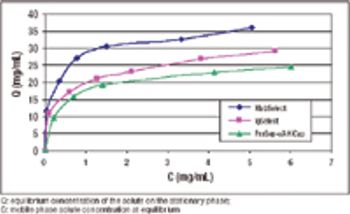
A stable alternative to Protein A chromatography.
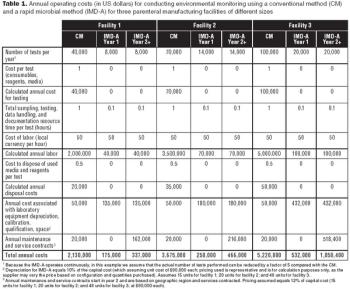
A case study implementing rapid microbiological methods.

A better method for trend analysis than CUSUM and control charts.
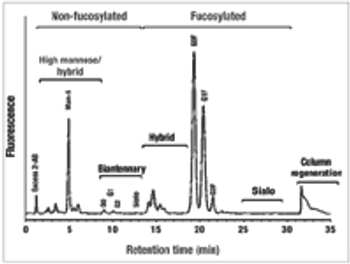
Select the best approach to determine critical quality attributes.

By following key strategies, companies can reduce the risk and increase the benefits of outsourcing analytical development and testing

Without a rigorous discussion of the pros and cons of QbD, its tremendous benefits will be lost.

This article reviews some of the commonly used approaches for process monitoring as well as the evolution of process monitoring in the Quality by Design (QbD) paradigm.
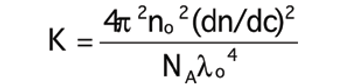
Can increase in ionic strength result in higher viscosity?
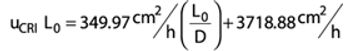
Robust packing procedures can improve process performance and increase resin lifetime.
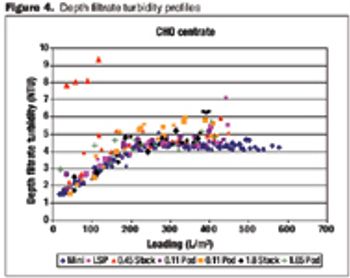
Data on the performance and variability of different formats.

QbD for QA? Try a two-step approach
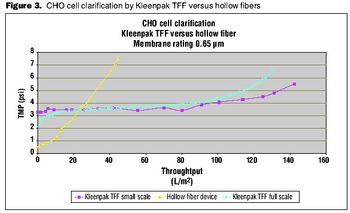
Choosing the right tools to enhance the process.
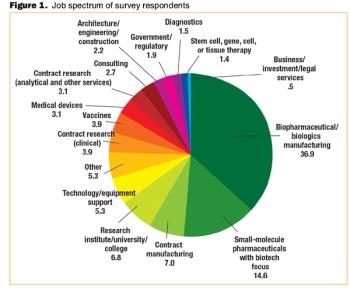
Will the global economic crisis affect your job? BioPharm International's third annual salary survey finds out.

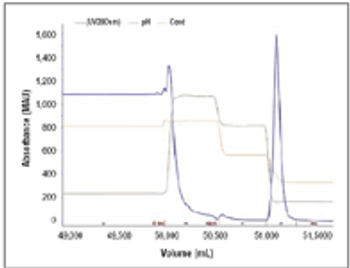
Results from a process developed for a commercial antibody.
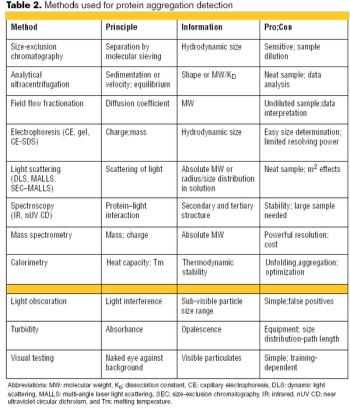
FDA perspectives on specs and effective control strategies.
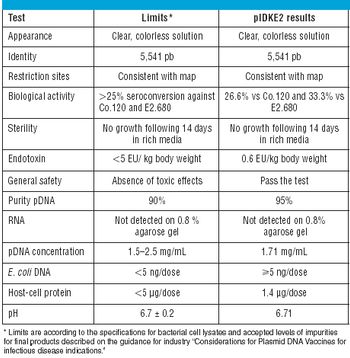
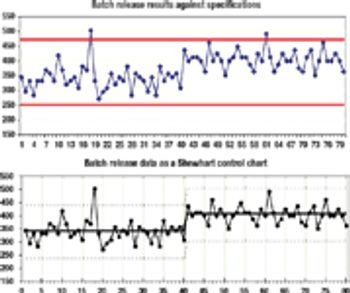
Improving your quality operations by using sound statistical principles.
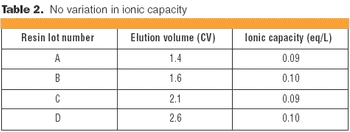
Understanding the impact on process performance.

In the context of process validation, the confirmation of a belief must be checked repeatedly, throughout the product lifecycle.
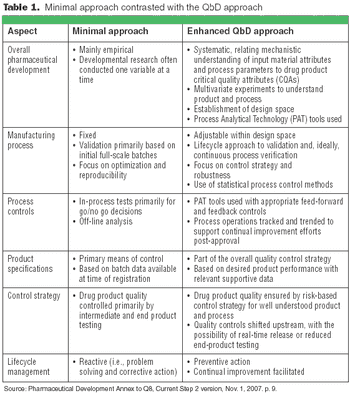
The principles of QbD can be applied to biotech development and manufacturing to help resolve many common issues. QbD scientifically provides a greater understanding of the complex relationships among product quality attributes, the manufacturing process, and clinical safety and efficacy by determining the various permutations of critical input variables that will keep the product within specification.
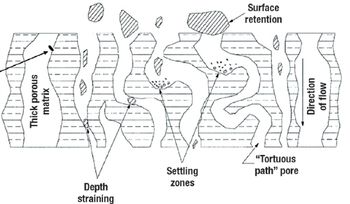
A comparison of primary harvest techniques.
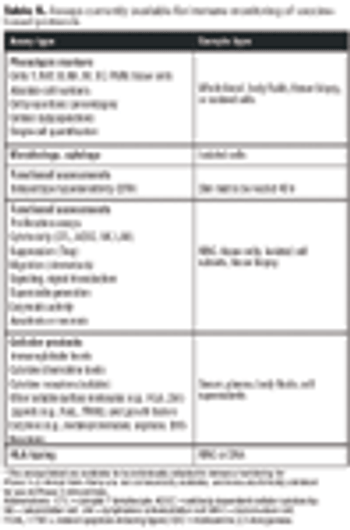
Emerging therapies pose challenges for standardizing QC.