
Both innovator and generics companies are using analytics to support comparability arguments.

Both innovator and generics companies are using analytics to support comparability arguments.
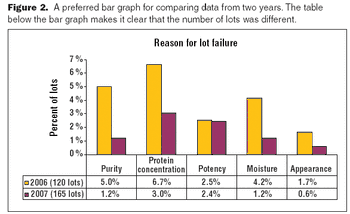
The key to a good graphical presentation is to select the method that best fits the data.

Design space concepts are key to a successful technology transfer.

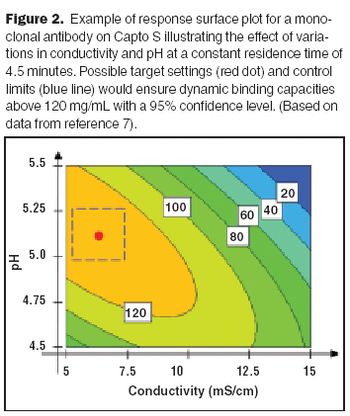
How the authors used design of experiments and quality by design principles to develop a hydrophobic interaction chromatography step.

Contrary to popular belief, the out-of-specification problem started years before the Barr Decision.

Regulatory agencies have evolved along with the biotechnology industry to define quality standards.

Multivariate data analysis can help biotech manufacturers deepen their process understanding.
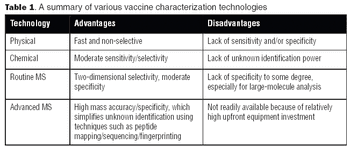
With the advent of high-resolution mass spectrometers and highly sensitive MS instruments, vaccine characterization has entered a new phase.

This flexible setup minimizes the number of purification process steps, buffers, and process components.
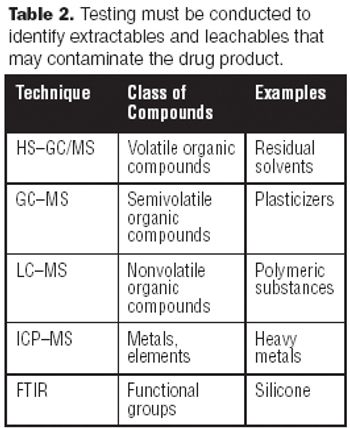
A tremendous amount of analytical testing is required to support a biopharmaceutical product from discovery, development, and clinical trials, through manufacturing and marketing. Numerous methods are used to fully characterize large molecules because of their complexity-characterizing them is significantly more difficult than it is for small molecules. Biopharmaceuticals are produced via living systems, i.e., E. coli, yeast, or mammalian cells, which require additional testing matrices.

Process monitoring ensures that the process performs within the defined acceptable variability that served as the basis for the filed design space.

The biopharmaceutical industry has gained a lot of experience in monitoring glycosylation, but still has a lot to learn about the structure–function relationship.

The United States Pharmacopeia (USP, Rockville, MD, www.usp.org) and the UK's National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC, Hertfordshire, UK, www.nibsc.ac.uk) are seeking participants in a study of analytical methods used by the industry to characterize and quantify oligosaccharides.

These articles encapsulate the past, present, and possible future of process-scale chromatography in biopharmaceutical production.
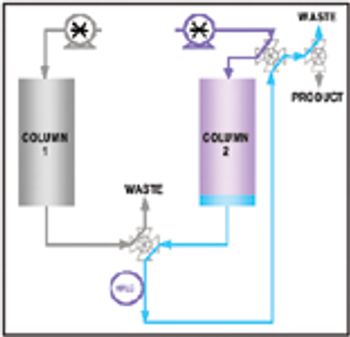
This article discusses how on-line high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) can measure product purity in the column eluent stream in near–real time. These data can then enable the automation and control of a purification column operation, thus reducing product variability, shortening process cycle time, and increasing yield. An example application demonstrates how on-line HPLC is used as a process analytical technology to ensure the process can accommodate variability in the separation while ensuring the product meets its critical quality attributes.
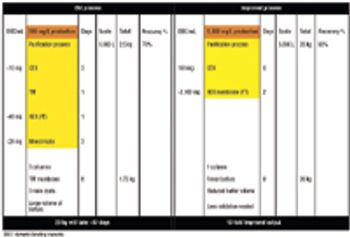
Affinity purification schemes for antibody production have certain limitations keeping up with cell culture expression levels as they reach and exceed 10 g/L. New downstream purification processes are based on low cost, long lasting, and high binding (40–100 mg/mL) cation exchange resins.

Vagueness in the ICH Q2A and Q2B guidelines necessitates effective protocol design and data analysis. For specificity (detection in the presence of interfering substances), the goal is statistical differences with meaningful implications on assay performance. Linearity (results directly proportional to concentration of analyte in the sample) is typically demonstrated via least squares regression. Accuracy (difference between measured and true values) usually is presented as a percent of nominal. Precision analysis is vital because it supports claims of accuracy and linearity. A well-designed experiment and statistically relevant methods will facilitate method validation in accordance with ICH guidelines.

Conducting an analysis of the 4 Ms-man, machine, methods, and materials-enables companies to identify the true root causes of deviations.

Increased resin stability can extend the number of cleaning cycles that can be performed in situ.

This article shows how Probabilistic Tolerance Intervals of the form, "We are 99% confident that 99% of the measurements will fall within the calculated tolerance limits" can be used to set acceptance limits using production data that are approximately Normally distributed. If the production measurements are concentrations of residual compounds that are present in very low concentrations, it may be appropriate to set acceptance limits by fitting a Poisson or an Exponential Distribution.

The first part of this article, published in the September 2006 issue, discussed general strategies for validation extensions to other test method components, laboratories and even different test methods.1This second part provides practical tips on how to maintain test method suitability long after the formal completion of analytical method validation (AMV) studies.

PerkinElmer Inc. (Wellesley, MA, www.perkinelmer.com) has acquired Avalon Instruments Limited (Belfast, Northern Ireland).

SOPs are written job aids that detail the procedure of how to do a specific job task correctly.

Reserve samples of test and control articles must be retained for at least one stability time point after the completion of the study.