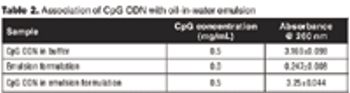
Adjuvant activity can be greatly improved by appropriate formulation of cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODNs).

Adjuvant activity can be greatly improved by appropriate formulation of cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODNs).
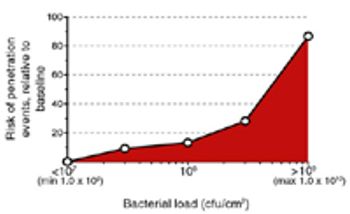
Filterability and bacterial retention must be verified very early in process development to ensure successful sterilizing filtration validation.
Adjuvant activity can be greatly improved by appropriate formulation of cytosine-phosphorothioate-guanine oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG ODNs).

We all know that experience is the best teacher. With H1N1, we have a great opportunity to learn important lessons.
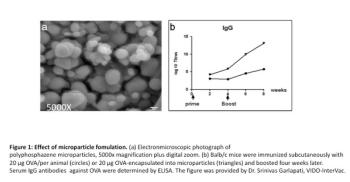
This article presents ongoing research at VIDO-InterVac for the development of safer and more effective adjuvants. These include adjuvants that stimulate innate immunity in the body and combination adjuvants.
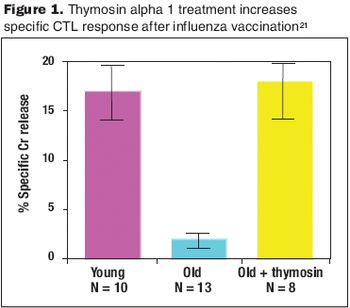
Clinical studies have shown that treatment with thymosin alpha 1 increases response to vaccination.
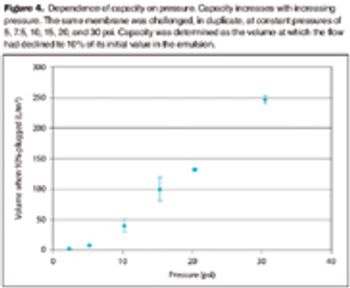
The viscosity of oily emulsions can reduce filter capacity and bacterial retention.
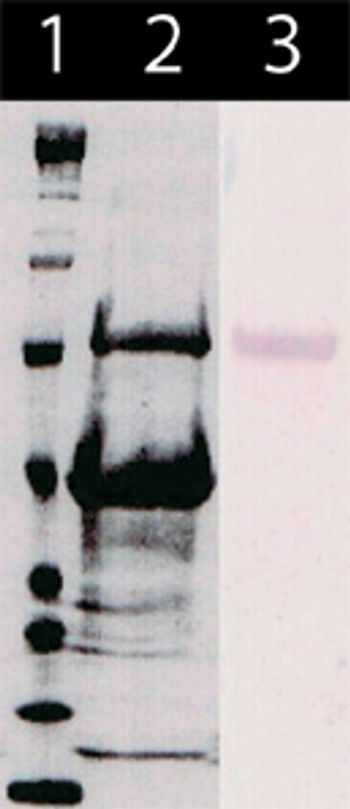
Recombinant vector technologies can improve the yield and lower the cost of egg-based influenza vaccine production.

The industry and government must collaborate to develop robust technologies and quicker, more flexible manufacturing approaches for vaccine development.
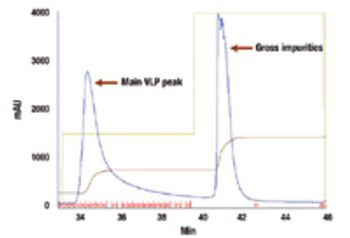
New technologies such as virus-like particles are promising weapons in the battle against pandemic influenza.

Membrane-based TFF technology can ease scale-up and provide a higher recovery percentage compared to conventional purification methods.

It is now possible to combine antigens with specific adjuvant systems to create more effective vaccines.
Needle-free vaccine delivery platforms can solve the problems of stockpiling, cold-chain management, and pandemic preparedness.

The truth is, we should have been afraid of H1N1, because the threat of a flu pandemic is real.

Biodefense start-up companies have an abundance of options when seeking funding.
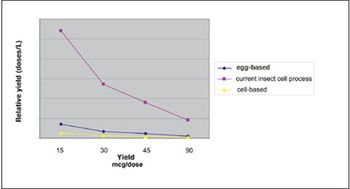
With virus-based production, vaccines can be available in 10-12 weeks.
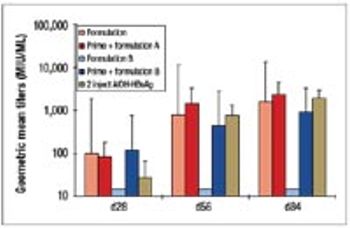
The disadvantages of the traditional vaccine regime (prime plus boost) have spurred the development of single-shot vaccines. This article describes the development and manufacture of a prototype single-shot vaccine that uses microspheres made from cross-linked modified dextran polymers for controlled release of the antigen.
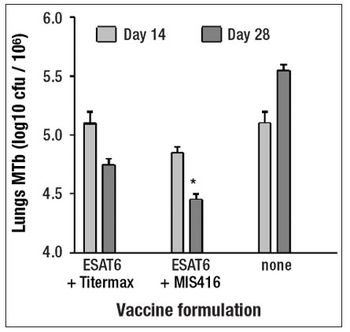
This article discusses the potential of MIS416 adjuvant, a vaccine adjuvant and immunogen co-delivery system, to provide adequate immunostimulation to overcome host factors that may limit the success of therapeutic vaccines.
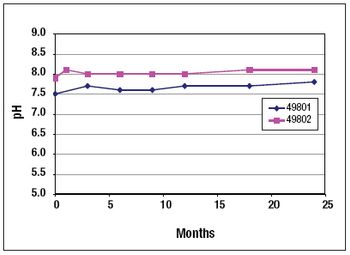
NeisVac-C is a polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine for use against Neisseria meningitidis serogroup C infection. The Phase 1 clinical formulation consisted of physiological saline, thimerosal, and aluminum hydroxide. The long-term stability data for both the PBS and saline formulations are presented in this article.

Interview with Roger Lias, president and group commercial director at Eden Biodesign, Inc.
This article discusses the production process of the major influenza antigen, hemagglutinin (HA), by rDNA methods in E. coli.

Interview with Magda Marquet, co-CEO and co-president of Althea Technologies
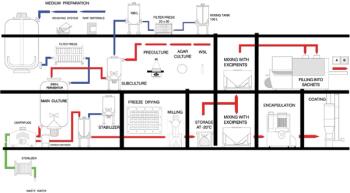
There are a number of specific characteristics to be considered when developing and manufacturing live bacterial vaccines.
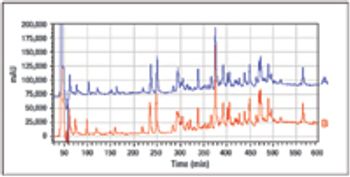
The Center for Molecular Immunology (Havana, Cuba) has been working on a novel cancer immunotherapy targeting the epidermal growth factor (EGF). The vaccine is composed of a chemical conjugate of EGF and a carrier protein (rP64k), designed to trigger an anti-EGF antibody response. The results of studies of molecular characterization, immunogenic activity, and clinical data are presented here.

To succeed in a pandemic, the industry must forge a preparedness plan to ensure adequate vaccines.