
The US FDA (Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) recently announced the availability of a draft guidance, entitled, Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System.

The US FDA (Rockville, MD, www.fda.gov) recently announced the availability of a draft guidance, entitled, Q10 Pharmaceutical Quality System.

The FDA issued MedImmune, Inc. (Gaithersburg, MD, www.medimmune.com), a warning letter for violating the agency's manufacturing rules and held off approving the company's influenza vaccine for use in children younger than age five until the problems are resolved.
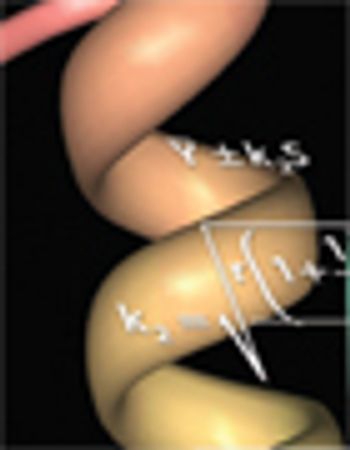
One goal of process characterization is establishing representative performance parameter ranges that can be used to set validation acceptance criteria (VAC). Characterization studies yield varying numbers of data points from multiple experiments, and may also include data generated at different scales (e.g., bench, pilot, and commercial), which add complexity to the analysis. Many statistical approaches can be used to set ranges from large data sets. As an example, we present the statistical considerations and techniques for setting validation acceptance ranges for a chromatography step used in purifying a recombinant protein. Performance parameter data from a combined data set consisting of 67 bench, six pilot, and three full-scale runs were analyzed using the statistical analysis software JMP (SAS Institute). The combined data set was used to compute tolerance intervals, so that sources such as scale and column feed material could be properly modeled. The resulting ranges were used to establish..

Process monitoring ensures that the process performs within the defined acceptable variability that served as the basis for the filed design space.

The biopharmaceutical industry has gained a lot of experience in monitoring glycosylation, but still has a lot to learn about the structure–function relationship.

The United States Pharmacopeia (USP, Rockville, MD, www.usp.org) and the UK's National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC, Hertfordshire, UK, www.nibsc.ac.uk) are seeking participants in a study of analytical methods used by the industry to characterize and quantify oligosaccharides.

Vagueness in the ICH Q2A and Q2B guidelines necessitates effective protocol design and data analysis. For specificity (detection in the presence of interfering substances), the goal is statistical differences with meaningful implications on assay performance. Linearity (results directly proportional to concentration of analyte in the sample) is typically demonstrated via least squares regression. Accuracy (difference between measured and true values) usually is presented as a percent of nominal. Precision analysis is vital because it supports claims of accuracy and linearity. A well-designed experiment and statistically relevant methods will facilitate method validation in accordance with ICH guidelines.

Conducting an analysis of the 4 Ms-man, machine, methods, and materials-enables companies to identify the true root causes of deviations.
The many benefits of disposable technologies, such as significant savings in time, labor and capital, as well as ease of scalability and flexibility, have led to the growing trend of adopting disposable technologies in bioprocess manufacturing processes.
Biopharmaceutical processes typically require a significant investment in equipment-often a substantial obstacle for start-up companies. The risk of drug development failure is often high, further limiting access to the required capital. Flexibility and lower capital outlays are required not only by start-up companies, but also by research organizations with multiple product lines and by companies requiring quick capacity increases. Disposable technologies offer the highest potential for these companies to meet their business requirements. With lower capital requirements and increased flexibility, disposables are an important part of these companies' risk management strategy.

This article shows how Probabilistic Tolerance Intervals of the form, "We are 99% confident that 99% of the measurements will fall within the calculated tolerance limits" can be used to set acceptance limits using production data that are approximately Normally distributed. If the production measurements are concentrations of residual compounds that are present in very low concentrations, it may be appropriate to set acceptance limits by fitting a Poisson or an Exponential Distribution.

The first part of this article, published in the September 2006 issue, discussed general strategies for validation extensions to other test method components, laboratories and even different test methods.1This second part provides practical tips on how to maintain test method suitability long after the formal completion of analytical method validation (AMV) studies.

Development reports document process development and support the design of validation experiments, yet in many firms training is not provided nor are expectations established. This article describes how project managers can help scientists master the art of report-writing.
Federal regulations are broad and open to interpretation. Most have not caught up with advancements in technology.

For decades now, it has been said that "the process is the product" for biologics. Great care and consistency must be applied in their upstream manufacture-during fermentation, harvest, and early purification-to preserve their complex structure, which confers their activity and specificity. As the product moves to late-stage purification, however, the relative concentration of impurities and altered product forms is diminished. Also, the final dosage form of most large molecule biopharmaceuticals is the relatively simple liquid formulation of parenteral dosage form. In contrast, manufacturing the solid dosage forms common for small-molecule drugs involves more complex processes, such as mixing dry powders, granulation, manufacturing controlled-release matrices, and tableting.

On August 12, 2003, Johnson & Johnson began recalling certain batches of its anemia drug, Eprex (epoetin alfa, sold as Procrit in the US), in most countries outside of the United States.

Air filtration also needs a filter integrity test method to guarantee the sterility of critical parameters.

Statisticians partner with technical experts to design statistically valid studies to construct the appropriate analysis.

Lyophilized, or freeze-dried, materials are challenging samples for quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) measurement because of the inability to open the container without corrupting the product. Near-infrared analysis presents itself as the QC method of choice for lyophilized materials due to its ability to penetrate glass or plastic containers to analyze the sample in a non-destructive manner. This study demonstrates the performance of a Fourier transform near-infrared (FT-NIR) spectrometer used in analyzing lyophilized samples of thrombin, a topical coagulant commonly used in the medical and dental fields. Key stability parameters for lyophilized thrombin include moisture and potency, which can be predicted simultaneously from a single spectrum using multivariate analysis.

Before designing cleaning procedures, it's vital to know all physical and chemical characteristics of the product ingredients.

Cleaning validation is a critical consideration in the pharmaceutical industry. Inadequate cleaning can result in contamination of drug products with bacteria, endotoxins, active pharmaceuticals from previous batch runs, and cleaning solution residues. Such contaminants must be reduced to safe levels, both for regulatory approval and to ensure patient safety.

Many industry professionals know that analytical testing for biopharmaceuticals for all raw materials, production in-process stages, and final containers must be validated, and they generally understand how this can be achieved. Many of us even understand the basic concepts of laboratory compliance and production process quality. However, how exactly are analytical test method performance and process robustness related and how do they depend on each other? Furthermore, how do we monitor and maintain the accuracy and reliability of analytical methods long after validation completion to ensure the suitability of these methods for measuring process quality?

Departure from dilutional similarity can be interpreted as evidence that the groups of organisms are not comparable or the preparations do not contain the same active compounds.

When data are not normal, a more efficient approach to monitor and control the performance of this assay requires transforming the data to a normal distribution. One of the most useful transformations was invented by Taguchi.